
Ever tried to read a contract and felt like you needed a secret decoder ring?That’s what legal jargon translation is all about. It’s the art of taking dense, often intimidating legal language and turning it into something a normal person can actually understand. This isn't just about swapping a few fancy words for simple ones; it's about making sure the document's core legal meaning stays perfectly intact while making it accessible to everyone, not just lawyers.
Get it right, and you build trust, slash risks, and make life easier for your clients and your team. Get it wrong, and you open the door to all sorts of trouble.
Why Clear Legal Communication Is a Business Imperative

Let's be blunt: complex legal language isn't just a nuisance—it’s a major business risk. When your contracts, agreements, or even internal policies are packed with impenetrable terms, you're practically inviting expensive misunderstandings and disputes. The fallout from one misunderstood clause can send shockwaves through your organization, hitting everything from your bottom line to your hard-earned reputation.
Think about a startup founder who’s just landed their first big funding round. They're staring at an agreement where a term like "pro-rata rights" is buried deep in the legalese. Without a clear translation, they might accidentally sign away a golden opportunity to maintain their ownership stake in future funding rounds. This isn't some far-fetched hypothetical; it’s a mistake that could cost them millions and happens all the time when jargon gets in the way of smart decisions.
To help you get started, here’s a quick-reference table that shows how some of the most common legal terms can be simplified. It's a great starting point for seeing just how much clearer things can be.
Common Legal Jargon and Plain English Equivalents
| Legal Jargon | Plain English Translation | Context of Use |
|---|---|---|
| Hereinafter | From this point forward | Used to introduce a shorter name for a party (e.g., "Acme Inc., hereinafter 'the Company'"). |
| Indemnify | Protect from financial loss | One party agrees to cover the other's costs if a specific negative event occurs. |
| Notwithstanding | Despite | "Despite anything else in this contract..." Signals that this clause overrides others. |
| Force Majeure | Unforeseeable circumstances | Frees both parties from liability if an extraordinary event (like a natural disaster) prevents them from fulfilling the contract. |
| Pro Rata | In proportion | A way of distributing something proportionally (e.g., distributing shares based on current ownership). |
| Liable | Legally responsible | Establishes who is at fault or must pay for damages. |
This table is just a glimpse into the world of legal translation. Once you start breaking down these terms, you realize how much more sense a document can make with just a few simple changes.
The Real-World Cost of Confusion
Misinterpreting legal documents isn't just a "what if" scenario. It has real, tangible consequences that can derail projects and sour relationships. For instance, a poorly explained non-disclosure agreement (NDA) might lead an employee to accidentally violate its terms, exposing the company to a lawsuit and compromising its intellectual property.
The global demand for clarity is massive. The legal translation services market alone was recently valued at around $1.3 billion, and it’s part of the much larger $41.78 billion global translation industry. This niche exists specifically to navigate the complexities of legal documents across 195 countries, which tells you just how critical this skill is worldwide. If you're interested, you can explore more data on the legal translation market size and growth.
A business that prioritizes clear legal communication isn't just being user-friendly; it's practicing smart risk management. Accessibility builds trust, empowers stakeholders, and creates a more transparent operational environment.
Beyond Convenience to Ethical Practice
At the end of the day, moving toward plain language is about more than just avoiding lawsuits. It's a matter of ethics and building trust. When a client, employee, or business partner can actually understand their rights and responsibilities without needing a law degree, you build a much stronger, more transparent relationship from the start.
This proactive approach pays off in several ways:
- Reduced Disputes: Clear agreements leave less room for ambiguity, which means fewer conflicts down the road.
- Faster Negotiations: When everyone understands the terms on the table, deals get done much faster.
- Enhanced Compliance: Employees are far more likely to follow policies they can actually understand, which cuts down on internal compliance headaches.
In a business world that's increasingly global, with cross-border agreements being the norm, being able to translate legal jargon is no longer just a "nice-to-have." It’s a core part of a sound business strategy, essential for protecting your interests and building a successful, sustainable company.
Foundational Principles for Accurate Legal Translation

Before you even think about changing a single word, it’s critical to get a handle on the core ideas that drive any good legal translation. This isn’t just about swapping out complex words for simpler ones. It’s a careful process of protecting a document’s legal power while making sure its intended reader can actually understand it.
The real goal here is precision, not just clarity. Mess up one word, and you could unintentionally shift obligations, get rid of important protections, or create loopholes that weren't there before. Think of a legal document less like a block of text and more like a finely tuned machine where every single part has a job to do.
Preserve the Core Legal Intent
Your number one job is to keep the document's original purpose intact. This means you need to put on your detective hat first, breaking down dense clauses to figure out the basic rights, responsibilities, or conditions they create. Don’t just hunt for synonyms; find the core legal action.
Take this common, but dense, legal phrase: "The Lessee shall be held responsible for any and all damages to the premises, save for normal wear and tear." A quick-and-dirty simplification might be "The renter pays for damages." But that’s a problem—it strips away a key protection for the renter.
A translation that’s much more on the mark would be: "You are responsible for paying for any damage you cause to the property. However, you are not responsible for damage that happens from normal, everyday use." This version is direct, easy to grasp, and, most importantly, legally the same.
The art of legal jargon translation lies in finding the balance between simplicity and legal integrity. Your job is to make the language accessible without diluting the legal substance that gives the document its power and enforceability.
Know Your Audience Inside and Out
Who is this translation for? The answer to that question completely changes how you should approach the task. Explaining a merger agreement to a board of directors is worlds away from breaking down a freelance contract for a graphic designer. Knowing your audience isn't just a good idea; it's essential.
Before you start writing, ask yourself these questions:
- What's their legal background? Are they a seasoned corporate lawyer or someone renting their first apartment?
- What are they trying to accomplish? Do they need to understand their risks, their duties, or how much they have to pay?
- What's the most critical piece of information for them? Your translation needs to spotlight what matters most to their situation.
For instance, if you’re simplifying a software license for a small business owner, you’d zero in on usage rights, renewal terms, and liability limits. But for a developer reading that same license, you’d probably put more emphasis on the clauses about intellectual property and open-source rules. This tailored approach is what makes the information genuinely useful. For a deeper dive into specific terms, our guide on legal jargon explained breaks down many common phrases.
Context Is Always King
Finally, never, ever translate a term on its own. The meaning of a legal word is almost always shaped by the text around it and the document's overall goal. The word "execute" might mean to sign a contract, or it could mean to carry out a specific task. Without context, your translation could be dangerously off base.
Always read the entire section—or better yet, the whole document—to get the full picture. This big-picture understanding empowers you to make smart choices, ensuring your simplified text accurately reflects its legal role in the agreement. By sticking to these three principles—preserving intent, knowing your audience, and respecting context—you'll build a solid foundation for any legal translation project.
Your Practical Framework for Translating Legal Documents
Alright, let's move from theory to action. This is where the real work of untangling legal jargon begins. To tackle any legal document effectively, you need a structured yet flexible game plan. Think of it less as a set of rigid rules and more as a reliable process that guides you from a wall of dense text to a clear, understandable message.
I’ve found it helps to break this down into three core phases: deconstruction, simplification, and verification. Each phase builds on the last, ensuring you not only make the text simpler but also keep its legal meaning completely intact.
This simple graphic lays out the heart of the process.
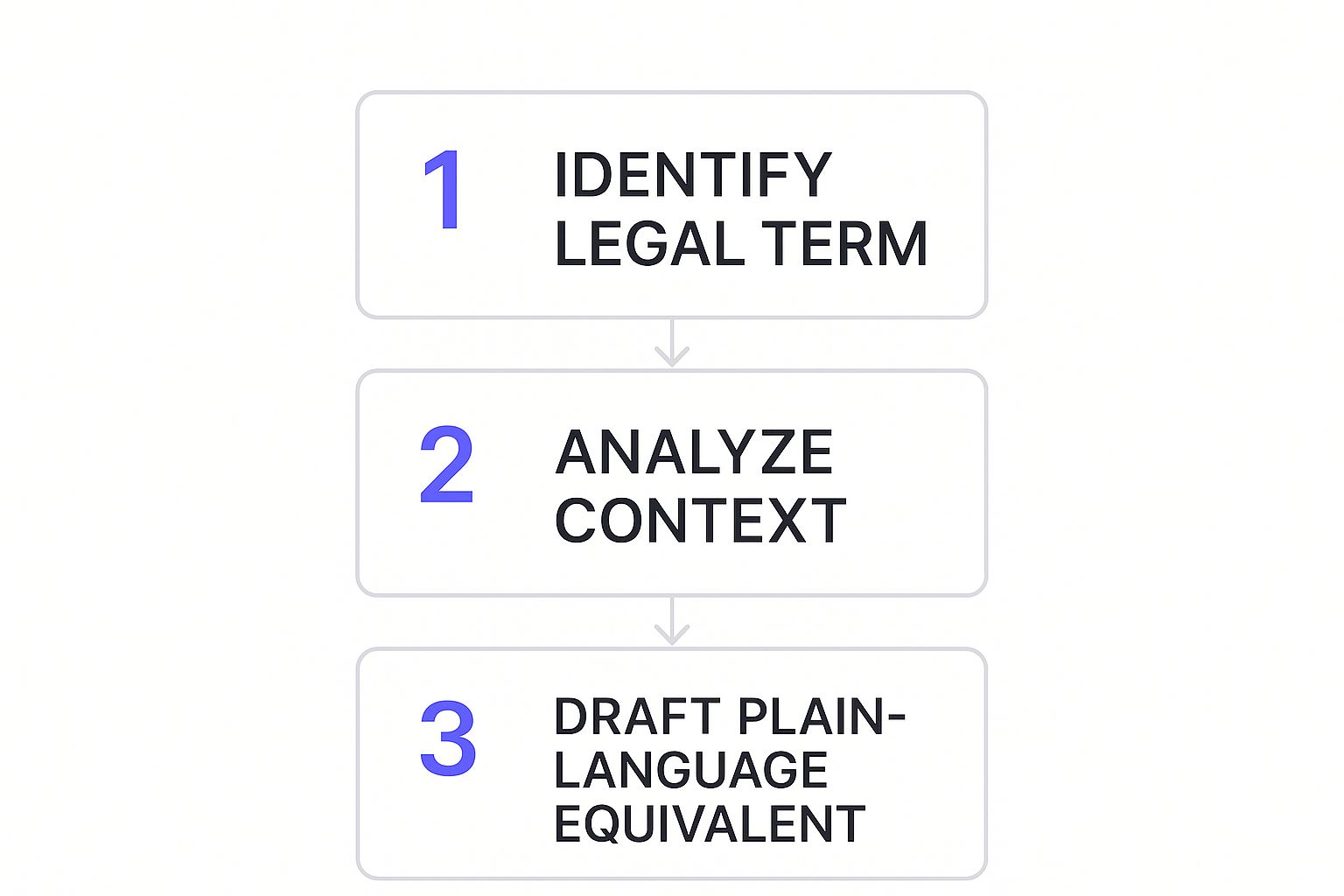
As you can see, the journey starts with focused analysis before any rewriting happens. That initial step is what keeps your final version accurate.
First, Deconstruct the Original Text
Before you can simplify anything, you have to break down the complex sentences. I like to think of it like a mechanic taking apart an engine—you need to see how all the pieces work together. Your goal is to pinpoint the essential components of each clause.
I always look for these four core elements:
- The Parties: Who is actually involved? (e.g., "the Lessor," "the Company," "the Employee")
- The Action: What must someone do or not do? (e.g., "shall provide," "is prohibited from," "must pay")
- The Conditions: Under what circumstances does the action kick in? (e.g., "in the event of a default," "upon termination of this agreement")
- The Outcomes: What’s the consequence if the action is (or isn't) taken? (e.g., "the contract becomes void," "a penalty of $500 is incurred")
Let's take a classic, dense sentence: "Hereinafter, the Consultant agrees to indemnify and hold harmless the Client against all claims arising from the Consultant's negligence." Breaking it down reveals the core parts: The Consultant (party) must protect (action) the Client if claims result from their carelessness (condition and outcome). Simple, right?
Next, Simplify With Purposeful Language
Once you’ve got the core meaning locked down, it's time to simplify. This part is all about swapping jargon for clear, direct language. One of the most powerful moves you can make is to use the active voice. Instead of the passive "Payment shall be made by the Client," just write, "The Client must pay." It’s shorter, clearer, and leaves no doubt about who’s responsible.
Another great tactic is to hunt down nominalizations—those clunky nouns made from verbs—and replace them with strong verbs. For instance, turn "make a determination" into "determine" and "provide assistance" into "assist." These small shifts make your writing feel more dynamic and much easier to digest.
Before: "The party of the first part is obligated to effectuate the remittance of funds to the party of the second part no later than the specified date." After: "You must pay us by the deadline."
The "after" version isn't just simpler; it's more direct and far less intimidating, which is essential for building trust. If you want more hands-on practice, you can translate legal jargon with tools that are great at spotting these kinds of improvement opportunities.
Finally, Verify for Legal Accuracy
This last step is absolutely non-negotiable. After you’ve simplified the text, you must double-check that it still carries the exact same legal weight as the original. Oversimplification is a real danger. I’ve seen situations where removing a single legally significant word changes everything.
Here are a few verification methods I rely on:
- Peer Review: Ask a colleague or another expert to review your simplified text against the original. A fresh set of eyes can catch nuances you might have missed.
- Back-Translation: Try translating your simplified version back into formal legal language. If the result lines up with the original's intent, you’re on the right track.
- Client Feedback: Show your version to the end-user and ask if they understand their rights and obligations. Their questions will quickly reveal any areas that are still unclear.
This verification phase is so much more than just proofreading. It's a critical quality control check to ensure your translation is both clear and legally sound. The demand for this skill is huge—the translation services market was valued at $60.68 billion in 2022 and is projected to hit $96.21 billion by 2032. You can dig into the drivers behind these numbers in this detailed industry report on Redokun.com.
Navigating The Common Traps Of Legal Simplification
When you're trying to make legal language easier to understand, you’re walking a tightrope. Lean too far one way, and the text is still a confusing mess. Lean too far the other way, and you could accidentally strip away its legal power. The path to clear, simple legal text is riddled with traps that can trip up even the most careful professional.
The two biggest dangers you'll face are over-simplification and the mishandling of legal "terms of art." Knowing how to spot and navigate these issues is what separates a clear, legally sound document from a potential disaster.
The Danger Of Over-Simplification
By far, the most common mistake is simplifying a phrase so much that you erase its essential legal meaning. A single word in a contract can hold a tremendous amount of weight, and if you carelessly remove it, you can completely change the rights and obligations of everyone involved. Legal battles often hinge on the specific phrasing of just one clause.
Let's take a real-world example. A freelance contract might state the client has "the sole and exclusive right to use the final deliverables." A quick attempt to simplify this could be "the client owns the work." That seems fine, right? But it's a huge mistake.
The original language might let the freelancer use early concepts in their portfolio. But "owns the work" could be interpreted to mean the client owns everything created during the project—including all the drafts, unused ideas, and preliminary sketches. A seemingly small change like that can quickly ignite a major dispute over intellectual property.
The goal is not to make the text as short as possible; it is to make the legal meaning as clear as possible. Losing a crucial detail for the sake of brevity is a mistake that can have significant financial and legal consequences.
Respecting Terms Of Art
Some legal phrases aren't just jargon; they're what we call "terms of art." These are specific terms with a precise, universally accepted legal definition that has been shaped by centuries of court rulings. You can't just swap them out for a simpler word without losing their meaning. Trying to "translate" them is not only difficult but also incredibly risky.
Think of words like force majeure, indemnify, or estoppel. These terms act as shorthand for complex legal concepts. For instance, replacing “indemnify” with a seemingly simple word like “protect” doesn’t come close to capturing the full legal obligation, which includes covering specific financial losses and even legal fees.
Here's how to handle these critical terms correctly:
- Identify Them: First, learn to recognize phrases that serve a specific, unchangeable legal function.
- Leave Them Intact: Whatever you do, don't try to rephrase or simplify the term of art itself.
- Explain Them Clearly: Immediately after you use the term, add a plain-language explanation of what it means in that context. For example: "The parties agree to indemnify each other. This means if one party is sued because of something the other party did, the responsible party will cover all legal costs and damages."
Understanding and avoiding these common translation pitfalls is a crucial skill. It’s about more than just good writing; it ensures that clarity never comes at the cost of legal accuracy, protecting everyone involved.
To help you stay on track, I've put together a quick-reference table that highlights these common issues and how to steer clear of them.
Common Translation Pitfalls and Solutions
This table breaks down some of the most frequent mistakes made when simplifying legal documents, the potential fallout, and practical strategies to avoid them.
| Common Pitfall | Potential Consequence | Avoidance Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Stripping Nuance | Altering rights and obligations, creating loopholes, or increasing liability. | Focus on clarifying meaning, not just shortening text. Keep words that define scope, like "sole" or "exclusive." |
| Misinterpreting "Terms of Art" | Invalidating a clause, losing legal protections, or creating an unenforceable agreement. | Identify and preserve the original term. Add a plain-language explanation immediately after its use. |
| Introducing Ambiguity | Replacing a specific legal term with a vague, general one, leading to future disputes. | Use concrete, specific language. Define what terms like "reasonable" or "timely" mean in context (e.g., "within 10 business days"). |
| Inconsistent Simplification | Simplifying a term in one part of the document but not another, causing confusion. | Create a glossary or style guide for the document. Review the final text for consistency in all simplified terms. |
By keeping these points in mind, you can approach the task with the caution it deserves. It’s a delicate balance, but getting it right ensures your documents are both accessible and legally robust.
Leveraging Technology in Legal Translation

Let's be honest—translating dense legal documents entirely by hand is a thing of the past. Today, the smartest approach marries human expertise with the right technology. The key is knowing which tools to use and understanding their limits to get a reliable result.
AI and machine translation (MT) platforms are fantastic for getting a first pass. They can churn through massive volumes of text in minutes, giving you a workable foundation. But they often miss the critical nuances and context that define a legal agreement. This is where you, the expert, come in.
Technology should be your assistant, not your replacement. Use it to handle the heavy lifting of a first draft, but always rely on your own expertise to ensure the final translation is legally sound and contextually accurate.
This hybrid model allows you to work quickly without sacrificing the precision that legal work demands.
The Right Tools for the Job
Beyond general translation AI, specialized software can completely change your workflow. These tools are built with the unique challenges of legal work in mind, offering much more focused help than a generic translator.
For large-scale projects, terminology management systems (also called termbases) are a game-changer. Think of them as a custom dictionary for your project. They ensure a crucial term like "indemnification" or "force majeure" is translated the same way across hundreds of pages, eliminating inconsistencies.
Another powerful category is contract analysis platforms. These tools use AI to scan documents and automatically flag vital information, such as:
- Critical dates and deadlines
- Financial obligations and payment terms
- Potentially risky or non-standard clauses
- The parties involved and their specific responsibilities
Using these tools helps you zero in on the most important clauses faster, so you can focus your expertise where it matters most. This is where the industry is headed. The global translation market is projected to grow from $42.62 billion in 2025 to $50.02 billion by 2033, a surge driven by these hybrid models. You can dive deeper into these trends in this detailed report on translation services.
A Smart, Hybrid Workflow
Ultimately, the most effective strategy is a hybrid one. Start by running your document through a solid AI tool to generate a baseline translation. Then, step in and use your knowledge to refine it, correcting errors and ensuring the original legal intent is perfectly preserved.
This method gives you the best of both worlds: the raw speed of automation combined with the irreplaceable insight of a human expert. It's the most efficient and reliable way to produce a clear, accurate, and legally sound translation every single time.
Frequently Asked Questions About Legal Jargon Translation
Even with a solid grasp of the basics, real-world questions always pop up when you start simplifying legal documents. This section dives into some of the most common queries we get from professionals, offering clear answers to help you feel more confident in your work.
Can I Use AI for All My Legal Translation Needs?
This is a big one. While AI is an incredibly powerful assistant, it absolutely should not be your sole resource for final translations. AI tools are fantastic for knocking out a first draft, identifying key terms, and flagging potential trouble spots.
But they can miss critical legal nuances and context.
Think of AI as a hyper-efficient junior paralegal. It does the initial heavy lifting, but a human expert must review and sign off on the output to ensure 100% legal accuracy. Relying on AI alone for a final document is risky—a tiny error in translation could have massive legal consequences.
When Is It Okay to Change a Legal Term?
You need to be extremely careful here. The golden rule is to avoid changing a "term of art"—a phrase with a specific, non-negotiable legal meaning like indemnify or force majeure. Swapping these out can strip the document of its legal power.
Instead of replacing the term, the best approach is to keep it and immediately add a plain-language explanation.
For example: "This agreement is subject to force majeure events. This means if an unforeseeable event like a natural disaster prevents either of us from fulfilling our duties, we won't be held liable." This preserves legal integrity while making sure everyone understands.
What’s the Difference Between Legal Translation and Interpretation?
Though they sound similar, they are two completely different professions.
- Translation deals exclusively with written text. A translator works with documents, contracts, and other written materials, usually with time to research and guarantee precision.
- Interpretation involves spoken language. An interpreter works in real-time—think courtrooms or depositions—converting spoken words from one language to another on the spot.
Legal translation is all about accurately converting written documents. Legal interpretation, on the other hand, is about facilitating live, spoken communication. Both demand deep legal and linguistic expertise, but the medium and skill sets are different.
For business owners dealing with contracts and policies, knowing this distinction is key. If you're looking for more guidance on the specific legal terms you might run into, check out our detailed guide on understanding legal jargon FAQ for business owners.
Tired of wrestling with confusing contracts? Legal Document Simplifier uses powerful AI to instantly translate dense legal documents into clear, actionable summaries. Upload your document and get the insights you need in minutes. Discover how you can simplify your legal review process today.