
When you're translating legal documents, it's not about a simple word-for-word swap. The real goal is to find what's called legal equivalence—conveying the core legal concept so it functions the same way in a different legal system. This takes a deep understanding of both the source and target legal frameworks to make sure the original rights and obligations hold up across borders.
The High Stakes of Legal Translation

Let's be clear: getting a single legal term wrong can be catastrophic. I’ve seen poorly translated phrases void multimillion-dollar contracts, completely derail corporate mergers, or sink a solid case in court. This isn't just a language issue. It's about preserving legal intent across entirely different justice systems, which is a monumental task.
The heart of the challenge is balancing linguistic precision with legal concepts that just don't have a direct counterpart. For example, a common law term like "estoppel" doesn't have a neat, one-to-one equivalent in many civil law systems. A literal translation would completely miss the legal weight it carries.
Why Precision Is Non-Negotiable
Every single word in a legal document is there for a reason. The tiny difference between "shall" and "may" can completely change a contractual obligation from a requirement to an option. Get it wrong, and the consequences pile up quickly.
Inaccurate translations often lead to:
- Financial Loss: Misinterpreted payment terms or liabilities can easily cost a company millions.
- Legal Disputes: Ambiguity from a sloppy translation is a breeding ground for litigation.
- Compliance Failures: If you misinterpret regulatory documents, you could be facing severe penalties.
For businesses operating on a global scale, these are daily challenges. Precise legal translation is absolutely essential for navigating complex financial issues, like overcoming double taxation when dealing with multiple jurisdictions.
The goal isn't just to make a document that sounds the same in another language. It needs to function the same legally in the target country. That requires a level of nuanced understanding that goes far beyond just knowing the vocabulary.
Ultimately, the stakes couldn't be higher. A mistake that seems minor on the surface can invalidate an entire agreement. That's why the guidance in this article is so critical for anyone who needs to get legal translations right.
Preparing for a Flawless Translation

A successful legal translation doesn't start with the first word you change. It begins long before that. Rushing in without a solid plan is a sure-fire way to end up with costly, embarrassing errors. The real foundation of an accurate translation is built on careful, deliberate prep work, starting with a deep dive into the source document itself.
First, you have to get a handle on its legal context. Is this a contract from a common law country like the United States, or does it come from a civil law system like France? That one distinction changes everything about how terms are interpreted and enforced. A good translator needs to grasp these nuances to find true legal equivalents, not just literal word-for-word swaps.
Just as critical is knowing who will be reading the final document. Are you translating for a judge? That requires a formal, precise tone. Or is it for a business partner, where clarity and practical understanding are the priority? The audience dictates the register and style. Before you begin, it’s also smart to have a basic grasp of what you're reviewing; our guide on how to read a contract is a great place to start.
Assembling Your Translation Toolkit
Once you’ve got the context down, it's time to gather your resources. This isn't about skipping steps; it's about preventing guesswork and ensuring everything stays consistent, especially on larger projects.
Your toolkit should always include a few key items:
- A Project-Specific Glossary: Make a list of key terms unique to the document, like "Indemnification" or "Force Majeure." Define them and decide on the official translation before you start.
- Client Clarification: Pinpoint any phrases or clauses that feel ambiguous or confusing. Get clarification from the client in writing to remove any doubt. This one small step can head off major disputes down the road.
- Relevant Style Guides: If your client has a corporate style guide covering their preferred tone, terminology, or formatting, get your hands on it. Consistency with their other official documents is non-negotiable.
A crucial takeaway here: the prep phase isn't optional. It’s the single most critical part of the entire process. Investing time upfront to nail down ambiguities and define key terms will save you countless hours and prevent the kind of mistakes that could invalidate the whole document.
By pulling these materials together and getting clear on the legal landscape, you're essentially creating a blueprint for a perfect translation. It’s a systematic approach that ensures every single term is handled with the precision the law demands.
Translating Concepts, Not Just Words

This is where the real art of legal translation truly shines. It’s about moving beyond a simple word-for-word swap, because legal systems are built on unique concepts, not just different vocabularies. The real goal is to find "legal equivalence"—the closest corresponding principle or outcome in the target legal system.
A literal translation often falls flat, sometimes spectacularly.
Take the common law term "estoppel." You won't find a neat, single-word equivalent in many civil law systems because the underlying legal principle just doesn't exist in the same way. A direct translation would be gibberish. Instead, you have to describe the concept itself: "a legal principle that prevents someone from arguing something or asserting a right that contradicts what they previously said or agreed to by law."
Finding Functional Equivalence
Your mission is to make sure the translated document functions identically in its new legal home. This requires a mental shift—stop looking for the right word and start conveying the intended legal effect. It's a tough but essential step for getting legal translations right.
Think about these common roadblocks:
- "Without prejudice": A standard phrase in common law settlement talks, but it lacks a direct counterpart in many languages. The translation has to explain the function: that the communication cannot be used as evidence in court.
- "Consideration": This is a bedrock concept in contract law in some countries, meaning something of value exchanged between parties. In systems that don't have this concept, you have to describe the reciprocal obligations to keep the contract valid.
The core task is to preserve the original legal meaning, even if it requires a descriptive phrase instead of a single term. You're translating the consequence and intent, not just the words on the page. This focus on conceptual accuracy is a huge driver behind the growth of the language services industry, which was valued at USD 60.68 billion globally in 2022.
Navigating Cultural and Legal Idioms
Every legal system comes with its own set of idioms and unique phrases baked into its culture. Translating these demands more than just legal knowledge; it requires real cultural fluency. Of course, it also helps to have a solid grasp of the base terms themselves—our guide explaining legal jargon is a great place to start.
For instance, a term like "Act of God" is widely understood in English-speaking legal circles to mean an unforeseeable natural disaster. But a literal translation could be confusing or even inappropriate in another culture.
The smarter approach? Use the standard local term for unforeseeable and uncontrollable events, like "force majeure," to achieve true conceptual alignment. This keeps the document’s formal tone and legal integrity intact.
Choosing Your Tools: AI vs. Human Expertise
When you need to translate legal terms, the whole "human versus machine" debate gets real, fast. Let's clear something up right away: the idea that AI can completely replace a skilled legal translator is a myth. AI tools, as smart as they are, often stumble over legal nuance, jurisdictional differences, and the actual intent behind a clause.
A much smarter approach is to see AI as a powerful assistant. It's brilliant at boosting consistency across stacks of repetitive documents, like standardized service agreements. It can also help you hunt down variations of a specific term in a mountain of text. This blend of machine speed and human intellect is where the real magic happens.
The Rise of AI in Legal Work
There's no denying that technology has massively sped up the translation process. In fact, AI and natural language processing can slash the time needed for bulk legal document translation by about 40%. With North America making up roughly 35% of the global demand—thanks to all our international trade and legal hoops—it's easy to see why these tools are gaining traction.
If you're thinking about bringing AI into your workflow, it helps to understand what's under the hood. The core technology, Natural Language Processing (NLP), is the engine that drives any machine translation tool you'll encounter.
This side-by-side look compares how human experts stack up against machine translation on accuracy and turnaround time.
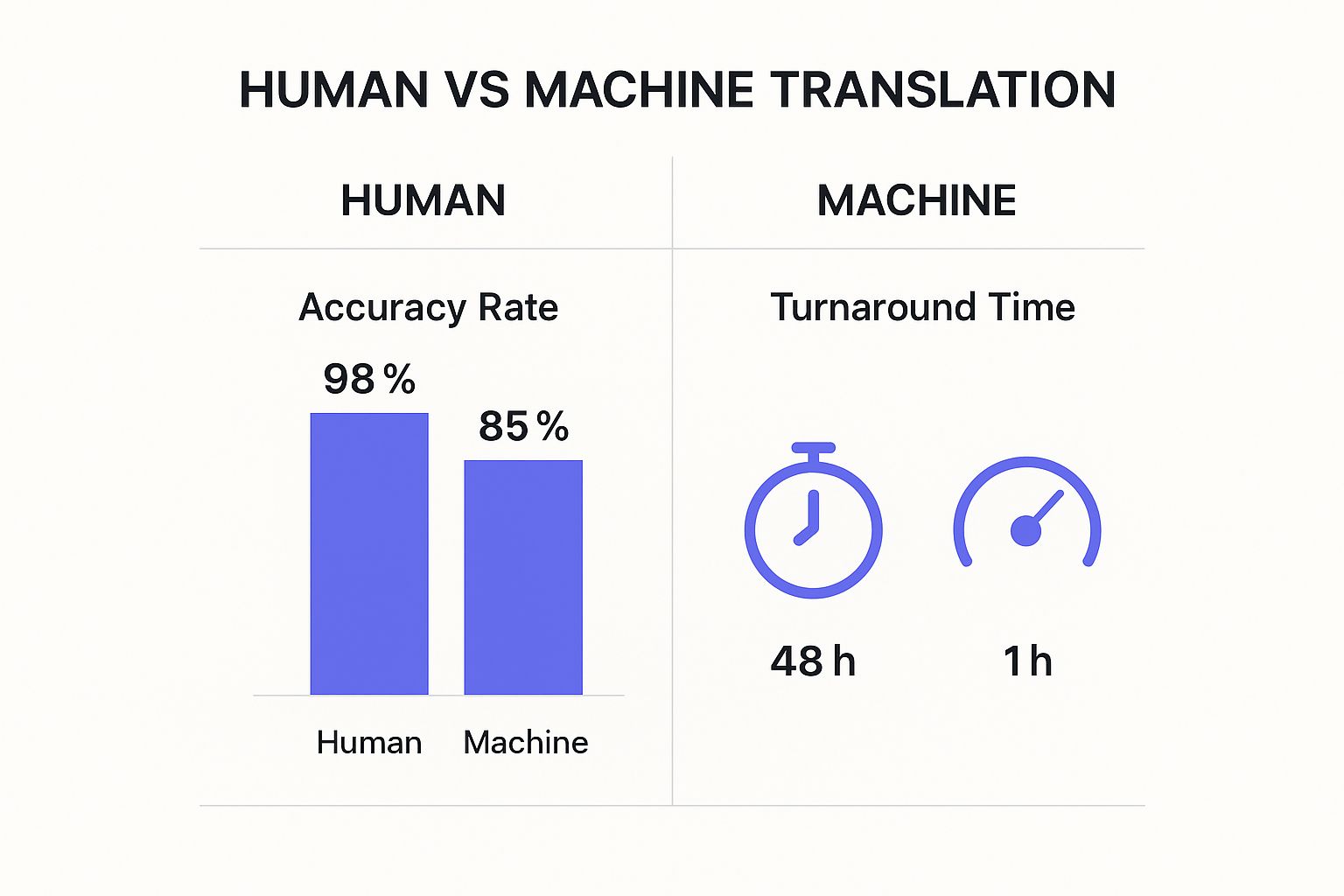
The numbers don't lie. While machines give you incredible speed, human translators deliver a much higher level of accuracy—and for high-stakes legal work, accuracy is everything.
So, how do you decide which tool is right for the job? Here’s a simple framework I use:
- AI-Powered Tools: These are your go-to for initial drafts of standardized agreements, scanning huge volumes of documents for key terms, or just keeping your terminology consistent. For more ideas, check out our guide on how businesses are using AI for legal documents.
- Certified Human Translators: When precision is non-negotiable, you need a human expert. Think court filings, patent applications, bespoke contracts, or any document where a single mistake could trigger severe legal or financial blowback.
AI Tools vs. Human Expertise in Legal Translation
Deciding between an AI tool and a certified human translator often comes down to the specific needs of your document. While AI offers impressive speed and cost-efficiency for certain tasks, the nuanced understanding and accountability of a human expert are irreplaceable for critical legal work. This table breaks down the key differences to help you choose the right resource for the job.
| Feature | AI Translation Tools | Certified Human Translator |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Varies; high for common phrases, lower for complex legal nuance. | 99%+ accuracy, understands context and intent. |
| Speed | Nearly instantaneous; can process thousands of words per minute. | Slower; typically 2,000-2,500 words per day. |
| Cost | Low, often a monthly subscription or pay-per-use model. | High, usually charged per word or per hour. |
| Contextual Nuance | Limited. Struggles with cultural context, tone, and ambiguity. | Excellent. Captures subtle meanings and jurisdictional specifics. |
| Consistency | High. Ensures uniform terminology across large documents. | High, but can require a glossary and style guide for perfect consistency. |
| Confidentiality | Varies by provider; requires careful vetting of data security policies. | High. Bound by professional ethics and NDAs. |
| Legal Accountability | None. The user is responsible for any errors. | High. Professionals are liable for their work and carry insurance. |
Ultimately, the choice isn't about which is "better" overall, but which is the appropriate tool for the specific legal document you're working with. AI is fantastic for preliminary work and standardized texts, but for anything that carries significant legal weight, the expertise and accountability of a human translator are essential.
The best strategy isn't choosing one over the other but knowing when to use each. Use AI for speed and volume, but always rely on a human expert for the final, critical review to ensure legal soundness and conceptual accuracy.
The Essential Quality Control Process
The first draft is never the final one, especially when you're wrestling with legal terminology. Once you’ve done the heavy lifting of translation, a strict, multi-layered review process is non-negotiable for any document with legal weight.
The cornerstone of this whole process is the "four-eye principle." It’s a simple concept with a huge impact: a second, independent legal translator reviews the entire text, comparing it line-by-line against the original source.
This isn't just a quick spell-check. The reviewer methodically cross-references your pre-made glossary to ensure every key term gets used consistently. They scrutinize grammar for absolute precision and, most importantly, double-check that the legal concepts hold up in the target jurisdiction. It’s this step that catches the subtle but critical errors a single translator, no matter how skilled, might overlook.
Your Quality Control Checklist
A structured approach is the only way to make sure nothing slips through the cracks. This second pair of eyes should systematically verify a few key things:
- Terminological Consistency: Is every mention of "liability" or "indemnification" a perfect match with the glossary definition? No exceptions.
- Grammatical Precision: Are conditional clauses, obligations ("shall" vs. "may"), and timelines translated with zero ambiguity? The smallest slip-up here can change everything.
- Legal Accuracy: Does the translation preserve the original legal intent and actually function correctly within the target legal system?
This rigorous quality control is fundamental to mitigating risk. It's no surprise that the legal translation services market is projected to grow from USD 1.4 billion in 2023 to around USD 2.8 billion by 2032. As you can find in market growth insights on dataintelo.com, this explosive growth highlights the rising demand for precision and the incredibly high cost of getting it wrong.
The final, indispensable step is a review by a legal professional who is a native speaker of the target language. This person confirms the document is not just linguistically perfect but legally sound and enforceable in its new home. Think of this final sign-off as your ultimate safeguard against costly misinterpretations.
Common Questions About Legal Translation
When it comes to translating legal documents, a few questions always seem to come up. Getting straight answers is key to making the right call and avoiding the kind of mistakes that spiral into serious legal trouble.
One of the big ones I hear all the time is whether a bilingual employee can just handle a legal contract. It might look like a smart way to save a few bucks, but it's an incredibly risky move.
Even if someone is perfectly fluent in two languages, they almost certainly don't have the specialized training in comparative law needed for this work. Legal systems have their own quirks and nuances from one country to another. A single misunderstood term could easily make a contract completely unenforceable.
Certified Translations and Legal Nuance
Another point of confusion is certification. People often ask what a "certified translation" actually is and when they really need one.
A certified translation isn't just a translated document; it's one that comes with a signed statement from the translator or translation agency. This statement, often called a Certificate of Accuracy, confirms that the translation is a complete and faithful version of the original.
You'll almost always need a certified translation when dealing with official bodies, such as:
- Submitting evidence to a court or government agency.
- Providing documents for immigration cases.
- Translating official records like birth certificates or university transcripts.
The real difference between general translation and legal translation comes down to consequences. A mistake in a novel is unfortunate. A mistake in a legal filing can lead to financial disaster or even the loss of liberty. This work demands an expert who understands not just the language, but the law itself.
That's why simply knowing the words isn't enough. Legal translation is its own discipline, blending linguistic precision with deep legal expertise to make sure every clause carries the exact same legal weight as the original.
Tired of wrestling with dense legal documents? Instead of burning hours trying to figure out what it all means, let Legal Document Simplifier handle it. Our AI-powered platform instantly turns complicated contracts into clear summaries, flagging key terms, deadlines, and risks. Make confident decisions in minutes, not days. Try it now and see how simple legal clarity can be.