
Navigating the Compliance Landscape
Staying compliant is crucial for any business, large or small. This business compliance checklist provides seven essential areas to review, helping you avoid legal issues and potential penalties. From business registration and taxes to data privacy and industry regulations, this list covers key compliance requirements for 2025. Understanding these concepts protects your business and fosters a secure operational environment. This checklist simplifies complex legal requirements, offering a straightforward path to compliance.
1. Business Structure and Registration Compliance
Ensuring your business is properly structured and registered is the cornerstone of any successful business compliance checklist. This crucial first step involves selecting the right business entity, registering with the appropriate authorities, obtaining necessary tax identification numbers, and maintaining ongoing compliance with relevant regulations at the federal, state, and local levels. Failing to address these foundational elements can lead to significant legal and financial repercussions down the line.
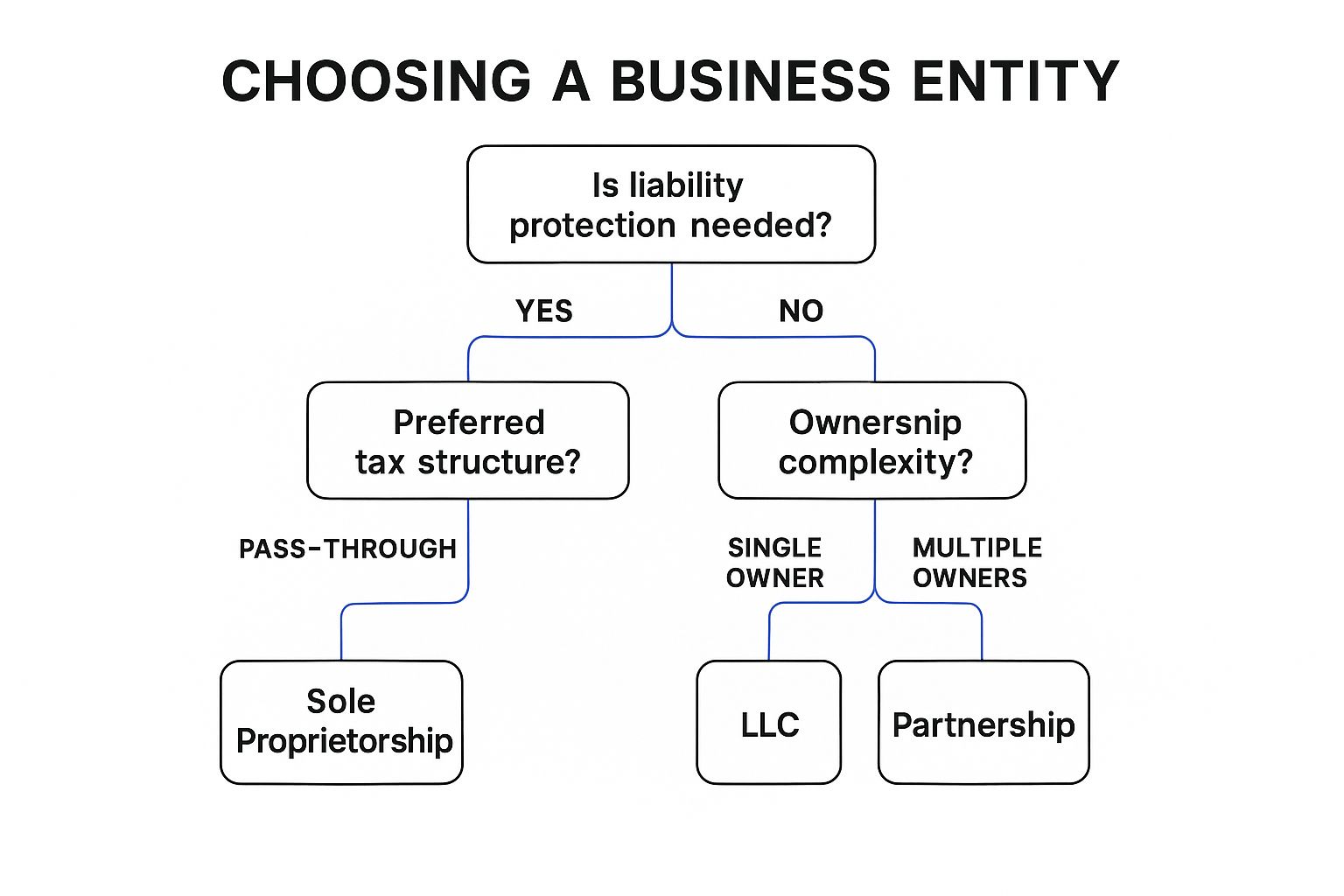
The infographic above presents a simplified decision tree to help you determine the most appropriate business structure. It starts by asking if you are operating solo or with partners. This initial question branches into further inquiries regarding liability protection, taxation preferences, and administrative complexity.
This process begins with choosing the optimal business structure for your needs, whether it's a sole proprietorship, partnership, Limited Liability Company (LLC), S-Corporation, or C-Corporation. Each structure offers distinct advantages and disadvantages related to liability protection, taxation, and administrative burden. For example, forming an LLC or corporation provides liability protection for business owners, shielding their personal assets from business debts and lawsuits. Learn more about Business Structure and Registration Compliance to delve deeper into the nuances of each entity type.
Once you've selected your business structure, you must register your business with the Secretary of State in the state where you operate. This typically involves filing articles of incorporation or organization and paying the associated filing fees. You'll also need to obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS, even if you don't plan to hire employees. An EIN is essential for various business activities, including opening a business bank account and filing taxes. If you plan to operate in multiple states, you’ll need to file foreign qualification paperwork in each additional state. Finally, maintaining ongoing compliance involves filing annual reports and maintaining proper corporate records, such as meeting minutes and operating agreements.
Successfully implementing the right business structure and maintaining compliance can offer numerous benefits. It provides liability protection for business owners, establishes a clear ownership structure and governance framework, and can create tax advantages when structured properly. Furthermore, being compliant builds credibility with customers, partners, and investors, fostering trust and confidence in your business.
However, it's crucial to acknowledge the potential drawbacks. Registration fees and ongoing compliance costs can be a burden, especially for startups and small businesses. Maintaining corporate records requires diligent paperwork and administrative effort. Navigating the different requirements across various jurisdictions can also be complex and time-consuming.
Consider the example of Apple Inc.'s conversion from Apple Computer, Inc. to a C-Corporation structure to support its growth and subsequent stock offerings. Similarly, Google's restructuring to form Alphabet Inc. as a holding company allowed them to better manage their diverse business ventures. Even small businesses benefit from utilizing registered agent services like CT Corporation or CSC to streamline compliance requirements across multiple states.
Tips for Ensuring Business Structure and Registration Compliance:
- Consult with Experts: Before selecting your entity type, consult with both a business attorney and accountant. They can help you determine the most advantageous structure for your specific circumstances.
- Compliance Calendar: Create a compliance calendar to track important deadlines for annual report filings, tax payments, and other compliance requirements.
- Compliance Software: Consider using compliance software like Corpnet or Harbor Compliance to streamline the process and ensure accuracy.
- Separate Finances: Keep your corporate and personal finances strictly separated to avoid legal and tax complications.
This item is crucial for any business compliance checklist as it establishes the legal foundation upon which your business operates. Properly structuring and registering your business not only mitigates legal and financial risks but also sets the stage for sustainable growth and success. Services like LegalZoom and resources from the Small Business Administration (SBA) and State Secretary of State offices have popularized and streamlined this process, making it more accessible to entrepreneurs and small business owners.
2. Tax Compliance and Reporting
Tax compliance and reporting is a crucial aspect of any business compliance checklist. It encompasses managing all required tax registrations, filings, payments, and reporting obligations at the federal, state, and local levels. This includes income taxes, sales taxes, employment taxes, and any industry-specific taxes that affect your business operations. Failing to properly address these requirements can expose your business to significant penalties and interest, potentially jeopardizing its financial stability. This is why it's a fundamental component of any robust business compliance checklist.
How it Works:
Tax compliance involves understanding and adhering to a complex web of regulations. It begins with registering your business with the appropriate tax authorities at each level of government where you operate. This might include obtaining an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS, registering for sales tax permits in states where you have a sales tax nexus, and complying with local tax ordinances.
Once registered, businesses must accurately calculate and pay various taxes. This involves meticulous record-keeping to track income, expenses, sales, and payroll. Regular filings, such as quarterly income tax payments and annual tax returns, must be submitted on time. Furthermore, businesses are responsible for withholding and remitting employee taxes, as well as reporting payments to independent contractors (1099s).
Features of Comprehensive Tax Compliance:
- Federal income tax compliance: Filing annual returns, making estimated tax payments.
- State and local tax registrations: Obtaining necessary permits and licenses.
- Sales and use tax collection and remittance: Charging, collecting, and remitting sales tax based on applicable regulations.
- Payroll tax administration: Withholding and remitting employee taxes (federal income tax, Social Security, Medicare).
- 1099 contractor reporting: Reporting payments to independent contractors.
- Property tax assessments: Paying taxes on business property.
- Industry-specific tax requirements: Addressing unique tax obligations relevant to your industry.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Large corporations like Walmart and Amazon demonstrate the complexity of tax compliance. Walmart manages tax compliance across over 50,000 tax jurisdictions, showcasing the need for sophisticated systems. Amazon has historically invested heavily in optimizing its sales tax collection systems, reflecting the importance of this area for e-commerce businesses. Smaller businesses often leverage software like QuickBooks or Avalara to automate aspects of tax compliance.
Pros:
- Prevents costly penalties and interest: Avoiding late filing penalties and interest charges.
- Allows for strategic tax planning opportunities: Identifying legal ways to minimize tax liabilities.
- Provides accurate financial insights for business decisions: Using tax data to inform business strategy.
- Builds credibility with financial institutions: Demonstrating financial responsibility.
Cons:
- Complex and frequently changing regulations: Keeping up with updates and changes in tax laws.
- Significant time commitment for record-keeping: Maintaining accurate and organized records.
- Potential cash flow challenges from tax payment schedules: Managing cash flow to meet tax obligations.
- Difficulty managing multi-jurisdiction requirements: Navigating varying tax laws across different states and localities.
Actionable Tips for Business Owners:
- Implement robust accounting software with tax reporting capabilities: Software like QuickBooks or Xero can automate many tax calculations and reporting tasks.
- Consider a tax compliance calendar with automated reminders: This helps prevent missed deadlines and late filings.
- Review sales tax nexus regularly, especially after the Wayfair decision: Ensure you understand your sales tax obligations in different states.
- Conduct quarterly tax planning meetings with your accountant: Discuss strategies for minimizing tax liabilities and optimizing tax efficiency.
- Document tax positions and maintain supporting records: This can be crucial in case of an audit.
Who Popularized This:
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS), state Departments of Revenue, accounting firms (Deloitte, PwC, EY, KPMG), and tax software companies (Intuit, Avalara) all contribute to the ongoing evolution and understanding of tax compliance.
In conclusion, incorporating tax compliance and reporting into your business compliance checklist is essential for long-term success. By understanding the requirements, leveraging available resources, and implementing a proactive approach, businesses can minimize risks and maximize financial health. Properly managing this aspect of your business contributes significantly to overall compliance and allows you to focus on growth and development.
3. Employment Law and HR Compliance
Navigating the complexities of employment law and HR compliance is a crucial aspect of any business compliance checklist. This involves adhering to a complex web of federal, state, and local employment laws and regulations that govern all aspects of the employer-employee relationship, from hiring and compensation to workplace safety, anti-discrimination, benefits administration, and termination procedures. Ignoring these regulations can lead to hefty penalties, reputational damage, and decreased employee morale. This is why prioritizing HR compliance deserves a prominent place on any business compliance checklist.

Key features of a robust HR compliance program include accurate employee classification (exempt vs. non-exempt, employee vs. contractor), meticulous wage and hour compliance according to the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), robust anti-discrimination and harassment policies in line with legislation like the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and Title VII of the Civil Rights Act, adherence to workplace safety standards as outlined by OSHA, comprehensive employee benefits compliance (including adherence to ERISA and COBRA), proper leave management under FMLA, and legally sound termination procedures.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Starbucks: In response to a highly publicized incident, Starbucks implemented comprehensive anti-bias training for all employees, demonstrating a commitment to addressing discrimination and fostering a more inclusive workplace. This is a powerful example of proactively addressing potential compliance issues and prioritizing employee relations.
- Microsoft: The tech giant has a structured approach to contractor classification, ensuring compliance with complex IRS regulations and mitigating the risk of misclassification penalties. This demonstrates a commitment to accurate and transparent employment practices.
- Patagonia: Known for its strong company culture, Patagonia offers model family leave policies that exceed legal requirements while maintaining compliance, fostering employee loyalty and well-being.
Pros:
- Reduced Legal Risk: Compliance minimizes the risk of costly employee lawsuits and government penalties.
- Improved Employee Morale and Retention: A fair and equitable workplace fosters a positive work environment, leading to higher employee satisfaction and retention rates.
- Safer Workplace: Adherence to OSHA standards and other safety regulations creates a safer work environment for everyone.
- Structured HR Practices: Compliance necessitates the implementation of structured HR processes, leading to greater efficiency and consistency.
Cons:
- Complexity: Navigating the patchwork of federal, state, and local laws can be complex and time-consuming.
- Constant Change: Regulations change frequently, requiring businesses to stay informed and adapt their practices accordingly.
- Documentation: Maintaining comprehensive employee records and other required documentation can be burdensome.
- Limited Flexibility: Strict adherence to regulations can sometimes limit flexibility in employment arrangements.
Tips for Maintaining HR Compliance:
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular internal HR audits using resources like the DOL's self-audit checklists.
- Employee Handbook: Develop and maintain an up-to-date employee handbook outlining company policies and procedures.
- Training: Provide regular training to managers and supervisors on compliance requirements and proper documentation.
- HR Software: Consider utilizing HR compliance software such as BambooHR or ADP to streamline processes and manage data efficiently.
- Secure Recordkeeping: Implement secure storage systems for sensitive employee records.
When and why should you prioritize this approach? Always. From the moment you hire your first employee, HR compliance is essential. Ignoring it can lead to significant legal and financial repercussions. By prioritizing employment law and HR compliance as a core component of your business compliance checklist, you protect your business, your employees, and your bottom line. This approach is essential for all businesses, regardless of size or industry.
4. Data Privacy and Security Compliance
Data privacy and security compliance is a critical component of any modern business compliance checklist. It involves implementing systems and processes to protect sensitive customer, employee, and business data in accordance with relevant laws and regulations. This encompasses a range of activities, from establishing robust data security protocols to managing data subject access requests. In today's interconnected world, where data breaches can have devastating consequences, prioritizing data privacy isn't just good practice – it's essential for survival.

This aspect of business compliance requires adherence to legislation like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the California Consumer Privacy Act/California Privacy Rights Act (CCPA/CPRA), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), as well as any industry-specific data protection requirements. This means businesses must understand the specific regulations that apply to them and implement the necessary measures to comply. Learn more about Data Privacy and Security Compliance. For example, a healthcare provider handling patient data needs to comply with HIPAA, while an e-commerce store processing credit card transactions must adhere to PCI DSS.
Features of a robust data privacy and security compliance program include clear data privacy policies and notices, consent management systems, strong data security protocols and encryption, established breach notification procedures, efficient data subject access request handling, diligent third-party vendor management, and comprehensive data retention and destruction policies. Implementing these features requires careful planning and execution.
Pros of strong data privacy and security compliance:
- Builds customer trust and brand reputation: Demonstrating a commitment to data privacy fosters trust among customers, enhancing brand loyalty and attracting new business.
- Reduces risk of data breaches and associated costs: Proactive data protection measures minimize the likelihood of breaches and the substantial financial and reputational damage they can inflict.
- Opens markets that require specific privacy certifications: Achieving recognized privacy certifications can open doors to new markets and business opportunities.
- Creates competitive advantage through stronger data governance: Effective data governance can lead to improved operational efficiency and better decision-making.
Cons of implementing data privacy and security compliance:
- Complex and evolving regulatory landscape: Keeping up with ever-changing data privacy regulations can be challenging, requiring ongoing monitoring and adaptation.
- Potentially significant technology investment: Implementing robust data security measures often necessitates investment in new technologies and infrastructure.
- May restrict certain data collection and marketing practices: Privacy regulations may limit the ways businesses can collect and use customer data for marketing purposes.
- Cross-border data transfer complications: Transferring data across international borders can introduce legal complexities and require specific safeguards.
Examples of successful data privacy and security compliance:
- Apple's Privacy Nutrition Labels provide transparency about app data collection practices, empowering users to make informed decisions.
- Salesforce's comprehensive approach to GDPR compliance demonstrates a commitment to data protection at a large scale.
- Small businesses utilizing platforms like OneTrust or TrustArc demonstrate how accessible privacy compliance management tools have become.
Tips for achieving data privacy and security compliance:
- Conduct regular data mapping exercises to understand information flows within your organization. Regular security audits are crucial for maintaining strong data protection. A comprehensive security audit checklist can help ensure all critical areas are covered.
- Implement privacy by design principles in all new product development, ensuring data protection is considered from the outset.
- Develop incident response plans for potential breaches, outlining clear steps to mitigate damage and notify affected parties.
- Train employees on data handling best practices, fostering a culture of data privacy within the organization.
- Consider obtaining privacy certifications like ISO 27701 or SOC 2 to demonstrate your commitment to data protection.
Data privacy and security compliance deserves a prominent place on any business compliance checklist because it is fundamental to building trust, mitigating risk, and operating ethically in today's data-driven world. Ignoring this crucial aspect can lead to legal penalties, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust. By proactively addressing data privacy and security, businesses can protect themselves and their customers while gaining a competitive edge.
5. Industry-Specific Regulatory Compliance
Staying on top of general business compliance is crucial, but equally vital, and often more complex, is navigating industry-specific regulations. This aspect of your business compliance checklist (#5) focuses on meeting the specialized requirements that apply to particular sectors like healthcare, financial services, food service, construction, transportation, or manufacturing. Ignoring these can lead to hefty fines, legal battles, and reputational damage, making it a crucial component of any comprehensive business compliance checklist.
Industry-specific regulatory compliance often involves a multifaceted approach encompassing licensing, permits, regular inspections, and adherence to stringent industry standards and practices. This means your business must not only understand the general rules of operation but also the nuanced regulations tailored to your specific field.
Features of Industry-Specific Compliance:
- Industry-specific licensing and credentialing: This can range from medical licenses for doctors to specialized certifications for construction contractors.
- Specialized reporting requirements: Different industries have unique reporting mandates, such as financial reporting for banks or environmental impact reports for manufacturing plants.
- Regulatory inspections and audits: Regular inspections from agencies like the FDA (for food and pharmaceuticals) or OSHA (for workplace safety) ensure businesses adhere to specific safety and operational standards.
- Product or service certifications: Certain industries require specific certifications for their products or services, demonstrating compliance with industry benchmarks. Think Energy Star ratings for appliances or organic certifications for food products.
- Industry-specific testing and quality assurance: Rigorous testing protocols are commonplace in sectors like pharmaceuticals and manufacturing to ensure product safety and efficacy.
- Specialized training and certification requirements: Employees in certain industries might require specific training and certifications, such as food safety handling certifications for restaurant workers.
Pros of Maintaining Industry-Specific Compliance:
- Builds credibility and trust: Demonstrating adherence to industry regulations fosters trust among customers and partners.
- Reduces liability and potential for regulatory sanctions: Compliance minimizes the risk of fines, lawsuits, and other legal repercussions.
- Creates barriers to entry: Meeting complex regulatory requirements can deter new competitors, benefiting established compliant businesses.
- Demonstrates commitment to industry best practices: Compliance signals a commitment to quality and professionalism within the industry.
Cons of Maintaining Industry-Specific Compliance:
- Often involves complex, technical requirements: Understanding and implementing industry-specific regulations can be challenging and time-consuming.
- Can require significant investment in specialized equipment or systems: Compliance may necessitate investments in specialized software, equipment, or personnel.
- Frequent regulatory changes requiring ongoing adaptation: Regulations can change frequently, requiring businesses to adapt quickly and efficiently.
- May involve multiple regulatory agencies with overlapping authority: Dealing with multiple regulatory bodies can create complexity and potential conflicts.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- FDA-regulated pharmaceutical companies like Pfizer implementing comprehensive Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
- Financial institutions like JP Morgan Chase maintaining complex compliance departments for SEC, FINRA, and banking regulations.
- Healthcare providers using specialized compliance software for HIPAA and HITECH requirements.
Actionable Tips for Maintaining Industry-Specific Compliance:
- Join industry associations: These organizations provide valuable regulatory updates, guidance, and best practice recommendations.
- Implement compliance management software: Specialized software can streamline compliance tasks and ensure adherence to regulations.
- Establish relationships with regulatory officials: Proactive communication with regulatory bodies can help resolve issues before they escalate.
- Conduct mock audits: Regular mock audits can help identify potential compliance gaps and areas for improvement.
- Document all compliance activities meticulously: Maintain thorough records of all compliance activities to demonstrate adherence to regulations.
Why This Item Deserves Its Place on the Checklist:
Industry-specific regulatory compliance is not just a box to tick; it's a foundational aspect of operating a legitimate and successful business. It protects your business from legal and financial risks, enhances your reputation, and builds trust with customers and stakeholders. While it can be complex, the benefits far outweigh the challenges, ensuring your business operates ethically and sustainably within its specific industry. This is why it is a critical element within any robust business compliance checklist.
6. Environmental and Sustainability Compliance
Environmental and Sustainability Compliance is a crucial aspect of any modern business compliance checklist. It refers to adhering to environmental regulations and standards regarding waste management, emissions, resource usage, chemical handling, and other environmental impacts. This isn't just about ticking boxes; it's about minimizing your business's environmental footprint and contributing to a healthier planet. Including this in your business compliance checklist demonstrates a commitment to responsible operations and helps avoid potential legal and reputational pitfalls.
Why is Environmental Compliance on the Business Compliance Checklist?
Ignoring environmental regulations can lead to hefty fines, legal battles, and reputational damage. Furthermore, proactive environmental management can unlock cost savings through resource efficiency and attract environmentally conscious customers. In today's world, sustainability is not just a trend; it's a business imperative.
How it Works:
Environmental and sustainability compliance involves a multifaceted approach covering several key areas:
- Environmental Permits and Registrations: Obtaining necessary permits for activities that impact air, water, and waste.
- Waste Management and Disposal Protocols: Implementing systems for proper handling, storage, and disposal of waste, including hazardous materials.
- Emissions Monitoring and Reporting: Tracking and reporting greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants.
- Hazardous Materials Handling Procedures: Developing safe procedures for handling and storing hazardous chemicals.
- Environmental Impact Assessments: Evaluating the potential environmental consequences of business activities.
- Sustainability Reporting and Disclosure: Publicly sharing information about a company's environmental performance.
- Energy Usage Monitoring and Efficiency Measures: Tracking energy consumption and implementing strategies to reduce it.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Patagonia: Known for its transparent and comprehensive environmental impact assessments, tracing the lifecycle of its products and advocating for environmental protection.
- Unilever: Their Sustainable Living Plan sets ambitious targets for reducing environmental impact across their operations and supply chain.
- Small Manufacturers using ISO 14001: Implementing an Environmental Management System (EMS) like ISO 14001 provides a framework for managing environmental responsibilities.
Pros:
- Prevents costly environmental penalties and remediation: Avoiding fines and cleanup costs associated with non-compliance.
- Enhances brand reputation and customer goodwill: Demonstrating environmental responsibility attracts customers and investors.
- Can reduce operational costs through resource efficiency: Optimizing resource use can lead to significant cost savings.
- Prepares business for increasing environmental regulations: Staying ahead of the curve ensures long-term compliance and competitiveness.
Cons:
- Complex technical requirements for monitoring and reporting: Meeting regulatory requirements can involve complex data collection and analysis.
- Potential for significant capital investment in equipment: Upgrading equipment to meet environmental standards can be expensive.
- Varying requirements across different jurisdictions: Navigating different regulations can be challenging for businesses operating in multiple locations.
- Rapidly evolving standards and expectations: Keeping up with changing regulations requires ongoing effort and investment.
Actionable Tips for Your Business Compliance Checklist:
- Conduct regular environmental compliance audits: Identify potential gaps and areas for improvement.
- Train designated employees as environmental compliance coordinators: Ensure someone is responsible for overseeing environmental compliance.
- Implement an Environmental Management System (EMS): A structured approach to managing environmental impacts.
- Document all waste handling, disposal, and environmental activities: Maintain detailed records for compliance reporting.
- Consider third-party environmental certifications: Demonstrate commitment to environmental best practices.
Popularized By:
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
- State environmental agencies
- International Standards Organization (ISO)
- Environmental consulting firms like ERM and AECOM
Environmental and Sustainability Compliance is an essential component of a comprehensive business compliance checklist. While it may present some challenges, the long-term benefits for your business, the environment, and your stakeholders far outweigh the costs. By incorporating these practices, businesses can contribute to a sustainable future while also strengthening their bottom line and building a positive brand image.
7. Financial and Accounting Compliance
Financial and Accounting Compliance is a crucial aspect of any business compliance checklist. It refers to the meticulous process of maintaining accurate financial records, implementing robust accounting controls, and ensuring that all financial reporting adheres to the relevant standards and regulations. This encompasses compliance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) for public companies, and other pertinent financial reporting requirements. This item deserves its place on the checklist because sound financial management is the bedrock of a sustainable and successful business. Without it, organizations risk penalties, reputational damage, and even legal repercussions.
This facet of compliance works by establishing a structured system for recording, analyzing, and reporting financial transactions. Standardized accounting practices ensure consistency and comparability. Financial controls and audit trails provide checks and balances to minimize errors and deter fraud. Accurate financial reporting systems generate reliable data for informed decision-making. Robust record retention policies ensure that crucial financial documentation is readily available when needed. Finally, fraud prevention mechanisms and the proper segregation of financial duties protect company assets and maintain the integrity of financial information. For publicly traded companies, securities compliance adds another layer of complexity and scrutiny.
Features of a Robust Financial and Accounting Compliance System:
- Standardized accounting practices: Implementing standardized procedures like GAAP or IFRS ensures consistency and allows for accurate comparison of financial data.
- Financial controls and audit trails: These are crucial for preventing errors, detecting fraud, and ensuring the integrity of financial information.
- Accurate financial reporting systems: Reliable systems are essential for producing accurate and timely financial reports.
- Record retention policies: Properly defined policies ensure that essential financial documents are readily accessible for audits, legal purposes, and internal reviews.
- Fraud prevention mechanisms: Implementing measures to deter and detect fraud is critical for protecting company assets.
- Securities compliance (for public companies): Publicly traded companies must comply with stringent regulations like SOX.
- Proper segregation of financial duties: This principle prevents conflicts of interest and reduces the risk of fraud.
Pros:
- Provides accurate financial information for strategic decision-making.
- Builds credibility and trust with investors, lenders, and stakeholders.
- Reduces the risk of fraud and financial misstatements.
- Facilitates tax compliance and simplifies financial audits.
Cons:
- Requires significant expertise and may necessitate consulting costs.
- May require investment in sophisticated accounting software.
- Time-intensive documentation and procedural requirements.
- Constant updates to standards may require system changes and retraining.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Johnson & Johnson's comprehensive SOX compliance framework demonstrates a commitment to rigorous financial reporting for a large, public company.
- Intuit, a company specializing in financial software, uses internal financial controls that mirror the functionality of the products they sell, showcasing a practical application of their expertise.
- Small businesses leverage cloud accounting platforms like Xero or QuickBooks, which offer built-in compliance features, demonstrating accessible solutions for businesses of all sizes.
Actionable Tips for Implementing Financial and Accounting Compliance:
- Implement accounting software appropriate for your business size and industry.
- Document financial procedures and controls in a comprehensive manual.
- Consider periodic reviews by external accounting professionals.
- Train multiple team members on compliance requirements to ensure redundancy and knowledge sharing.
- Maintain detailed audit trails for all financial transactions.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
Financial and Accounting Compliance is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process that should be integrated into the daily operations of every business, regardless of size or industry. From the moment a company begins financial transactions, adhering to these principles is crucial. Neglecting these aspects can lead to significant financial and legal risks.
Learn more about Financial and Accounting Compliance
This section on Financial and Accounting Compliance within a business compliance checklist is indispensable for ensuring the long-term health and success of any organization. It provides a framework for financial transparency, accountability, and ultimately, informed decision-making. By adhering to these principles, businesses can mitigate risks, build trust, and focus on achieving their strategic objectives. This detailed understanding is particularly helpful for our target audience – small business owners, freelancers, in-house legal teams, individuals managing legal agreements, and startup founders – who need to ensure they're meeting legal and financial obligations efficiently and effectively. They can benefit from understanding the complexities of financial compliance and the tools and strategies available to manage it successfully.
7-Point Business Compliance Checklist Comparison
| Compliance Area | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Business Structure and Registration Compliance | Medium - Legal setup and ongoing filings | Moderate - Legal, accounting, and software | Legal protection, clear governance, tax benefits | Startups, expanding businesses, multi-state ops | Liability protection, tax advantages, credibility |
| Tax Compliance and Reporting | High - Complex, frequently changing laws | High - Accounting, software, professional help | Avoid penalties, accurate financials, tax planning | All businesses with tax obligations | Penalty avoidance, financial insight, credibility |
| Employment Law and HR Compliance | High - Complex regulations & frequent updates | High - HR personnel, training, software | Reduced lawsuits, improved morale, safer workplace | Companies with employees | Legal risk reduction, employee retention, compliance consistency |
| Data Privacy and Security Compliance | High - Evolving laws and technical setup | High - Technology, training, privacy tools | Customer trust, data breach reduction, market access | Businesses handling sensitive data | Brand reputation, breach risk reduction, competitive advantage |
| Industry-Specific Regulatory Compliance | Very High - Technical, multi-agency oversight | High - Specialized equipment and consulting | Industry credibility, reduced sanctions, competitive edge | Regulated sectors (healthcare, finance, food) | Trust building, liability reduction, market barriers |
| Environmental and Sustainability Compliance | Medium-High - Technical monitoring required | Moderate-High - Equipment, training, audits | Avoid penalties, brand enhancement, cost savings | Manufacturing, resource-intensive businesses | Environmental protection, operational savings, reputation |
| Financial and Accounting Compliance | High - Expertise and ongoing updates | High - Skilled accountants, software, audits | Accurate reporting, fraud prevention, compliance | Public companies, financially-regulated firms | Financial accuracy, fraud reduction, investor confidence |
Staying Ahead of the Compliance Game
Navigating the complexities of business compliance can feel overwhelming, but with a structured approach, it becomes manageable. This business compliance checklist has covered key areas, from fundamental aspects like business structure and tax compliance to more specialized areas such as data privacy, industry regulations, and environmental considerations. We've also touched upon the crucial elements of employment law, financial and accounting compliance, and the importance of understanding your obligations related to each. Mastering these concepts isn't just about checking boxes; it's about building a solid foundation for your business, minimizing risks, and fostering trust with stakeholders. By proactively addressing these compliance requirements, you protect your business from potential legal issues and financial penalties, allowing you to focus on growth and innovation.
The most important takeaway is that compliance is not a one-time event but a continuous process. Regulations evolve, and your business will too. Regularly review your business compliance checklist and seek expert advice when needed. This proactive approach will save you time, money, and potential headaches down the line. By prioritizing compliance, you create a more resilient, trustworthy, and ultimately more successful business.
Ready to simplify your compliance journey and ensure you're always ahead of the curve? Legal Document Simplifier can help you organize your business compliance checklist, understand complex legal jargon, and manage your documents efficiently. Visit Legal Document Simplifier today to learn more and streamline your compliance efforts.