
In simple terms, what does notwithstanding mean in law? Think of it as the ultimate trump card in a legal document. When you see this word, it signals that the clause following it takes priority over any other conflicting statements. It essentially means "in spite of" or "despite."
Unpacking the Power of Notwithstanding

Ever feel like legal documents are written in another language? You're not alone. One of the most powerful—and often confusing—words you'll run into is notwithstanding. Its main job is to cut through the noise and prevent arguments by setting a clear hierarchy of rules.
Imagine a complex agreement packed with dozens of clauses. It's easy for some of them to unintentionally contradict each other. That's where "notwithstanding" comes in. By inserting a phrase like "notwithstanding any other provision in this agreement," a lawyer creates an override switch. This move tells everyone involved exactly which rule wins, eliminating ambiguity right from the start.
Why This Word Matters
The strategic use of notwithstanding is crucial for a few key reasons:
- Conflict Resolution: It nips potential contradictions in the bud before they can escalate into costly legal battles.
- Prioritizing Clauses: It ensures the most critical terms of an agreement are given the precedence they deserve.
- Enforcing Intent: It makes the original intent of the contract drafters unmistakably clear to a court.
This one word can save countless hours and resources by making sure the intended order of operations is respected.
Key Takeaway: When you see a "notwithstanding" clause, stop and pay close attention. It’s a deliberate signal that the information following it supersedes any other related rule in the document.
To make its role even clearer, here's a quick look at how it functions in different legal scenarios.
Notwithstanding At A Glance
This table breaks down how "notwithstanding" acts as an override in various legal contexts, from everyday contracts to constitutional law.
| Legal Context | Primary Function | Common Example |
|---|---|---|
| Contracts | To ensure a specific clause overrides any conflicting general terms. | "Notwithstanding anything to the contrary, the Tenant is solely responsible for all repairs." |
| Statutes/Laws | To allow a new law to operate despite older, conflicting legislation. | A new environmental law might apply "notwithstanding the provisions of the 1985 Water Act." |
| Constitutions | To permit legislation to temporarily bypass certain guaranteed rights. | Canada's Charter allows laws to operate "notwithstanding" certain fundamental freedoms. |
As you can see, its purpose is always the same: to establish one rule as the final word, regardless of what other parts of the document might say.
Why Lawyers Use This Powerful Legal Term
Lawyers reach for the word "notwithstanding" for one simple reason: to create absolute certainty and head off future arguments before they can even start. Think of a complex agreement like a machine with lots of moving parts. Sometimes, a few of those parts—or clauses—might accidentally contradict each other, bringing the whole machine to a grinding halt.
This is where "notwithstanding" acts like a master override switch.
By adding a phrase like "notwithstanding any other provision in this agreement," a lawyer is essentially flagging a specific rule and declaring it the winner. It creates a clear hierarchy, making sure one critical term is respected above all others. This simple move cuts through any potential confusion right from the get-go.
Preventing Costly Conflicts
The ultimate goal here is to defuse potential conflicts before they blow up into expensive legal battles. A single, well-placed "notwithstanding" clause can save a company thousands in legal fees and countless hours by making the contract's primary intention undeniable.
Without it, two competing clauses could open the door to different interpretations, laying the groundwork for a major disagreement or even a lawsuit. To get a better sense of how these disputes take shape, you can learn more about what makes up a valid cause of action and see just how much damage ambiguity can do.
This one word is a powerful risk management tool. It shields the most important agreements in a contract from being accidentally watered down by other, more general statements.
Ensuring Certainty in Legal Writing
At the end of the day, the power of notwithstanding is all about enforcing certainty. Legal drafting is a precision sport, and every word counts. For anyone interested in the finer points, you can explore some expert tips on how to write clear and effective legal documents. Using exact language like "notwithstanding" is a fundamental technique for building contracts that are solid, clear, and far less likely to be challenged in court.
How Notwithstanding Works in Everyday Contracts

Alright, let's pull this concept out of the legal textbooks and into the real world. You probably run into "notwithstanding" clauses more often than you think—they pop up in rental agreements, freelance contracts, and even the terms of service you click "agree" on.
Its job is always the same: to make one specific rule the top priority.
Think about a standard apartment lease. It might have a broad clause saying, "The landlord is responsible for all property maintenance." But buried a few pages later, you could find a sentence that starts with, "Notwithstanding the foregoing, the tenant is solely responsible for all garden and lawn care."
That little phrase is a big deal. It acts as a trump card, carving out a specific exception to the general rule and making sure a key duty doesn't get lost in the shuffle. It cuts through any potential confusion before it starts.
This is how "notwithstanding" prevents ambiguity in contract law. It’s a bright, flashing sign that says, "Pay attention! This part overrules anything else you read that might seem to conflict with it." This ensures everyone is on the same page about the most critical terms.
Prioritizing Key Obligations
At its core, "notwithstanding" is a tool for managing risk and flagging the non-negotiables. It draws a clear circle around a particular responsibility, making it impossible to miss.
Here are a couple of common scenarios:
- Freelance Contracts: A contract might state a general 30-day payment cycle for invoices. But a crucial clause could add, "Notwithstanding any other term, a 50% deposit is due upon signing and is non-refundable." This protects the freelancer's upfront time and effort.
- Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs): An NDA could have a general rule allowing information to be shared with legal counsel. A "notwithstanding" clause can create a powerful exception, stating that certain trade secrets cannot be disclosed to anyone, for any reason, without getting written consent first.
Practical Tip: When you see "notwithstanding" in a contract, treat it like a spotlight. It's deliberately highlighting a rule that is meant to be absolute, overriding any general statements you might have read earlier in the document.
Spotting this term is your cue to understand the full scope of your duties and rights. It’s directly tied to the promises being exchanged, which are the heart of any agreement. To dig deeper into that, it's helpful to also learn about the legal definition of consideration in contract law, the concept that makes a contract legally binding.
The Impact of Notwithstanding in National Law
The power of “notwithstanding” isn't just for private contracts; it plays a much bigger, high-stakes role in shaping entire legal systems. In the world of constitutional and statutory law, governments use this term to pass legislation that operates in spite of other laws or even fundamental rights.
Think of it as a legislative trump card. When a government passes a law “notwithstanding” an older statute, it’s creating a clear legal hierarchy. It’s a signal that the new law is the supreme authority on a particular issue, preventing older laws from getting in the way. This is a powerful tool for updating legal frameworks without having to go back and repeal every single conflicting piece of old legislation.
This mechanism is key for adapting to new challenges and ensuring the government can respond to society's changing needs. But its most potent—and controversial—use is when it’s aimed at constitutional rights.
The Canadian Notwithstanding Clause
Canada provides a prime example of this power in action. The term notwithstanding is an override mechanism that allows certain laws to take precedence even if they conflict with other legal rights. This is most famously seen in Section 33 of the Canadian Constitution, known as the 'notwithstanding clause,' which was part of the Constitution Act of 1982.
This clause gives federal or provincial legislatures the power to pass laws that operate "notwithstanding" specific rights guaranteed in the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms. For a deeper dive, you can explore some excellent analyses of administrative law matters online.
This infographic helps visualize how a general law gets superseded by a notwithstanding clause, which then overrides protected rights.
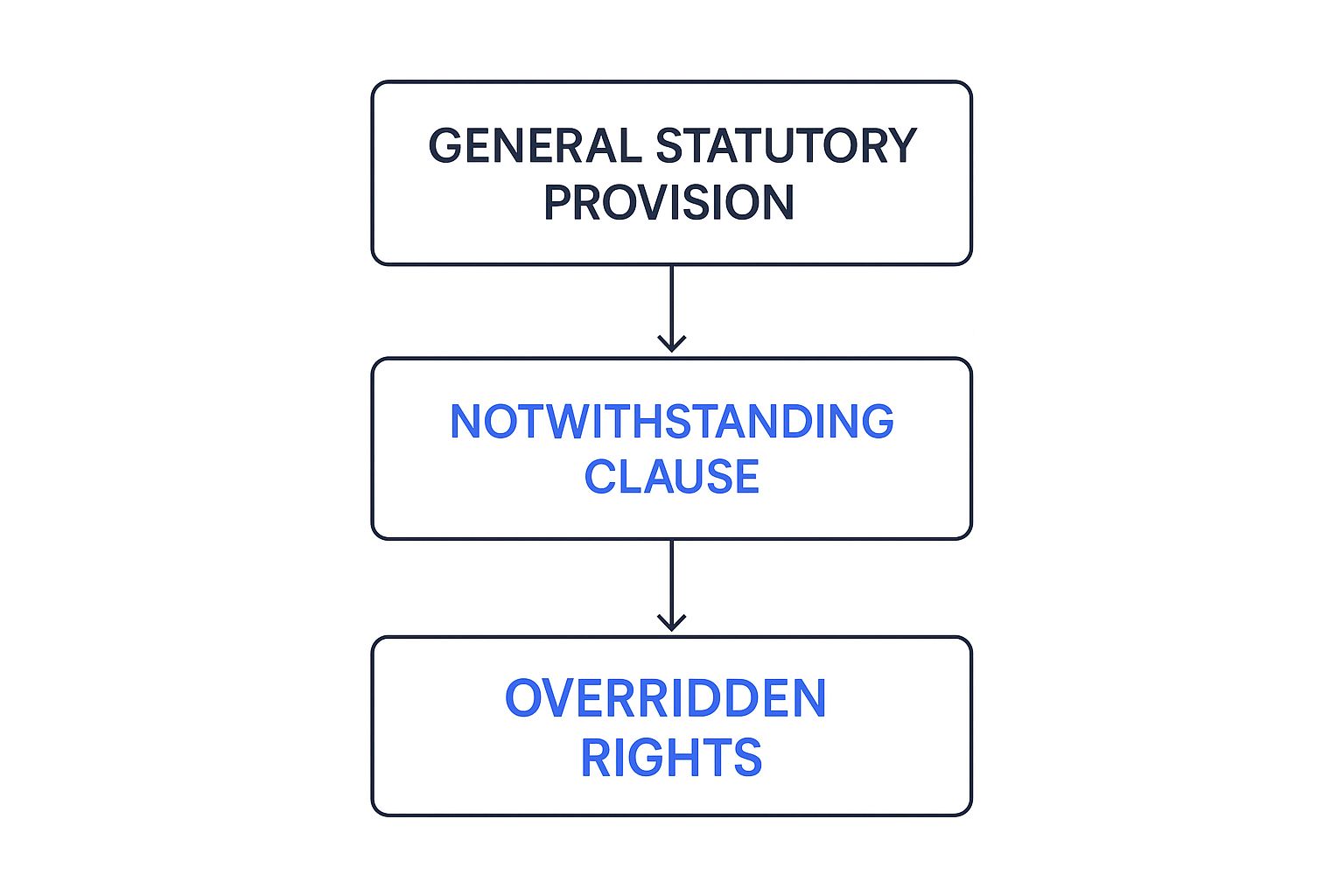
As the diagram shows, the clause acts as a legal bridge, allowing legislative power to bypass foundational rights.
Naturally, this provision sparks intense debate. It forces a tough conversation about the balance between democratic legislative power and the individual freedoms that are supposed to be the bedrock of a nation. It brings up complex questions about government authority, similar to those that arise when you explore what jurisdiction means and who really has the power to make and enforce laws.
What to Remember About "Notwithstanding"

As we've covered, getting a handle on what notwithstanding means in law is a game-changer for reading any legal document. At its core, the word is an override switch, making sure one specific rule wins out over any others that seem to clash with it.
Think of it as the ultimate legal trump card. Its whole purpose is to cut through potential confusion and establish a clear pecking order for the rules in a contract, law, or even a constitution.
When you see "notwithstanding," it’s a deliberate signal to stop and pay extra attention. The clause that follows is meant to be the final say on that issue, no matter what other general statements appear elsewhere.
Its Core Functions
To keep it simple, here’s what "notwithstanding" is really doing:
- It Creates Certainty: Its main job is to shut down potential conflicts before they ever become a problem, making the document's intent perfectly clear.
- It Prioritizes Rules: It puts a big, flashing sign on one provision, elevating it above any other competing clauses. It’s the non-negotiable part.
- It Manages Risk: Lawyers use it strategically to shield the most critical parts of an agreement from being watered down by other language.
By demystifying this single word, you empower yourself to better understand your rights and obligations. The term may seem intimidating, but its goal is simple: to ensure a specific rule is followed without exception.
Always treat a "notwithstanding" clause as a spotlight. It’s highlighting a rule that demands your full attention.
Still Have Questions About Notwithstanding?
Even after you get the hang of what "notwithstanding" means in theory, a few practical questions always seem to pop up. It’s one of those words that can make your pulse quicken when you spot it in a document you’re about to sign.
Let's clear up some of the most common sticking points. This will help you feel more confident when you encounter this powerful little word in the wild.
How Is Notwithstanding Different From Subject To?
This is a fantastic question because these two phrases are essentially polar opposites. They both manage the relationship between different clauses, but they give completely different instructions.
Think of it like traffic signals in your contract:
- "Notwithstanding" is a green light. It tells a clause, "Go ahead, you have priority." It overrides any conflicting rules (the red lights) it might encounter elsewhere in the document.
- "Subject to" is a yield sign. It signals that a clause needs to slow down and give way to a more dominant provision. It’s lower on the food chain.
For example, a bonus clause might state it is "subject to the company meeting its annual revenue targets." This means the bonus takes a backseat; it only happens if the revenue target is hit. A "notwithstanding" clause would do the exact opposite, making sure its own rule is followed, no matter what the revenue clause says.
The Bottom Line: "Notwithstanding" creates a trump card—a superior clause that wins any conflict. "Subject to" creates a subordinate clause that is governed by another. Getting this difference right is crucial for understanding who owes what in any legal agreement.
Can a Notwithstanding Clause Be Challenged in Court?
Yes, absolutely. While a "notwithstanding" clause is designed to be a legal heavy-hitter, it isn’t invincible. Courts are meant to enforce clarity, so they won't just ignore it, but it can be challenged and overturned in specific situations.
A judge might throw out a "notwithstanding" clause if it is:
- Hopelessly Ambiguous: If the clause itself is so poorly written that no one can figure out what it means, it fails its primary mission: to create clarity. In that case, a court may decide it's unenforceable.
- Against Public Policy: You can't use a contract to break the law. A clause that says, "Notwithstanding any labor laws, the employee agrees to work without safety equipment," would be tossed out immediately because it promotes an illegal act.
- Unconscionable: If a clause is so outrageously one-sided and unfair that it shocks the conscience, a court might step in. This often happens when there's a huge power imbalance, like between a massive corporation and an individual.
Challenging these clauses is never simple and always depends on the specific facts and local laws. But it’s good to know that even this powerful legal tool has to play by the rules of fairness and legality.
What Should I Do if I See This in a Contract?
First off, don't panic. But definitely pay attention. A "notwithstanding" clause is a bright red flag waving at you, signaling that a specific rule has been given special importance.
Here's a simple, methodical approach:
First, read the clause very carefully to pinpoint exactly what rule it’s creating. What does it want to happen?
Next, hunt down the other clauses it might override. Look for general rules elsewhere in the contract that seem to conflict with this specific, high-priority one.
Finally, figure out the impact on you. Does this trump card fundamentally change the deal in a way that puts you at a disadvantage?
If you’re even slightly unsure about what it means for you, this is the perfect time to get a legal professional involved. A quick consultation can save you from a world of headaches down the road.
Navigating dense legal language is tough, but you don’t have to do it alone. Legal Document Simplifier uses AI to instantly translate complex contracts into simple summaries you can actually use. Upload your document today and get the clarity you need to make confident decisions. See how it works at Legal Document Simplifier.